What Are the Gonorrhea?
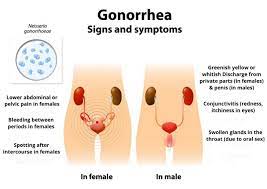
You may have been infected with gonorrhea if you've experienced one of the common symptoms. However, gonorrhea is often hard to detect and treat. Listed below are some of the signs and symptoms of gonorrhea, as well as the proper way to treat it. If you're experiencing any of these symptoms, you should seek medical attention as soon as possible.
Signs and symptoms
There are several common signs of gonorrhea, including a thick, bloody discharge from the vagina or penis. The amount and color of the release depend on how the bacteria have spread throughout the body. A shot may also contain blood, and it may be excruciating. Although this infection is rarely severe, it should be investigated to prevent further complications. If you suspect you have gonorrhea, you should seek treatment as soon as possible.
Diagnosis
A woman with gonorrhea should visit her physician. The infection usually affects the cervix and is asymptomatic in 50% of cases. However, the disease can manifest as a mucopurulent discharge and friable cervical mucosa. Other common symptoms include abdominal pain, dyspareunia, and pruritus. Diagnosis of gonorrhea is vital in preventing complications like PID and other pregnancy-related problems. For example, PID is associated with an increased risk of tubal scarring and can result in ectopic pregnancy in 40 percent of women with cervical infection.
Treatment
Antibiotics are widely used for the treatment of gonorrhea. Despite advances in antimicrobial resistance, N. gonorrhea persists. In adults, a combination of two drugs with different mechanisms of action is often used for improved efficacy and prevention of the emergence of antimicrobial-resistant gonorrhea. The choice of the mixture depends on the site of infection and the potential for resistance.
Symptoms of gonorrhea
If you're experiencing burning or redness in your genitals, you may suffer from gonorrhea. If you suspect you may have this infection, it is best to get checked by a healthcare provider. You'll likely be asked about your sexual history and symptoms. A urine test and pelvic exam can help confirm the diagnosis, but you should also get a throat culture to rule out anal infections.
Infertility
Gonorrhea is an infection that affects the female reproductive tract. This bacterium thrives in the cervix and fallopian tubes and can also affect men. When untreated, it can cause inflammation of the sperm duct, which prevents sperm from entering a woman during intercourse. Additionally, untreated epididymitis can lead to scarring of the fallopian tubes, preventing sperm from entering a female during intercourse. However, infertility due to gonorrhea is not yet a confirmed cause of tubal pregnancy in men.
Scarred fallopian tubes
If untreated, gonorrhea can cause pelvic inflammatory disease, permanently damaging a woman's reproductive system. Treatment for this infection involves antibiotics, and untreated gonorrhea can lead to scarring in the fallopian tubes, which increases the risk of pregnancy and chronic pelvic pain. A healthy pregnancy begins when a sperm fertilizes an egg inside the fallopian line. The fertilized egg moves to the uterus within a few days, and the embryo settles into the lining of the uterus and develops for 9 months.
Ectopic pregnancy
While there are no definitive symptoms of ectopic pregnancy caused by gonorrhea, the infection may spread into the uterus or fallopian tubes. This can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease and, if left untreated, ectopic pregnancy. In addition to the symptoms associated with gonorrhea, women with the pelvic inflammatory disease are more likely to develop pelvic pain and an increase in the risk of ectopic pregnancy.



