What Are the Causes of Scabies?
Scabies is not life-threatening, but prompt medical intervention is essential to break the disease cycle and prevent complications. Aggressive scratching can lead to secondary bacterial infections. However, the rash caused by scabies is not a cause for alarm. Read on to find out what causes this condition and what to do if you suspect you have it. You can prevent scabies from recurring with the following tips.
Symptoms
While pets cannot directly transmit scabies, they can harbor a mite that carries the disease. These mites are spread through close physical contact and sharing bedding and clothing. Humans can develop scabies from animal mites, but they cannot reproduce on human skin. Once an animal mite gets under the skin of a human, it dies after a few days. There are several ways to avoid scabies, though.
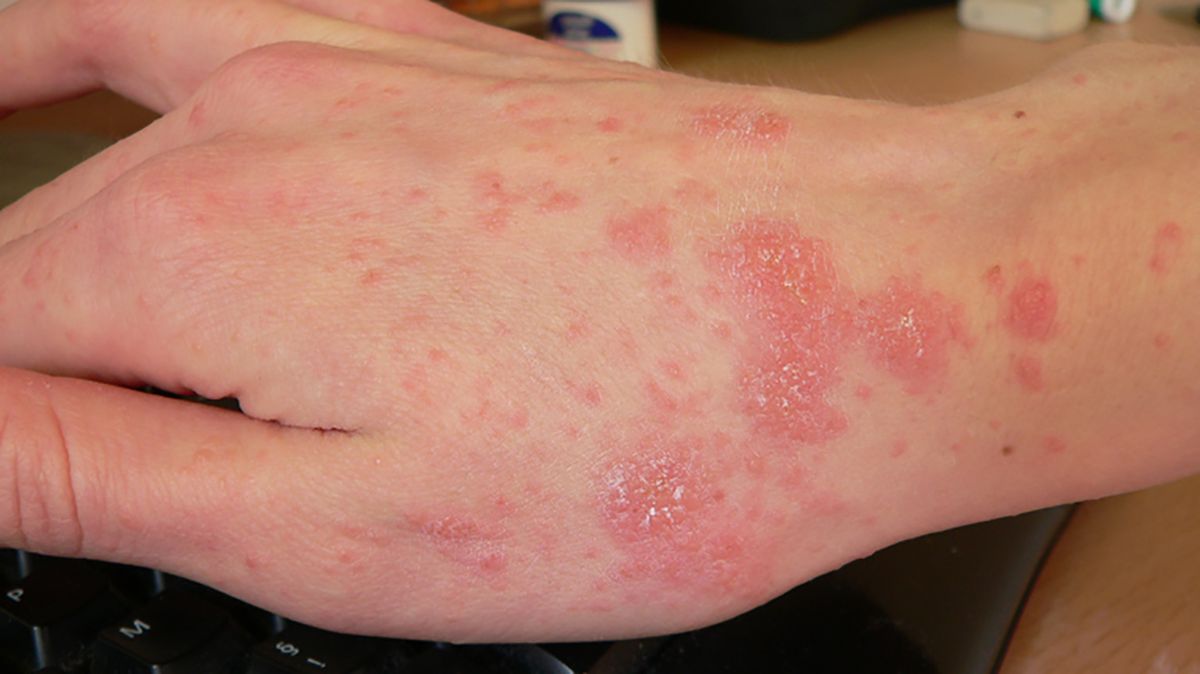
The primary symptom of scabies is an itchy rash. Itching is the most common sensation, and the mites may be easily spread through extended skin-to-skin contact. While handshakes do not apply the mites, holding hands for five to ten minutes can. Sexual contact is also a common way to spread scabies and is quickly passed from one person to another. Scabies is rapidly spread within a household.
Causes
The human species is vulnerable to scabies infestation. The parasite Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis burrows into the skin and triggers an allergic response, resulting in intense itching. If left untreated, scabies can lead to skin sores, septicemia, heart disease, and chronic kidney disease. Unfortunately, the underlying causes of scabies are still poorly understood.
The infection is usually transmitted from animal to human by contact with infected animals. It is contagious and highly infectious. The symptoms of scabies may include crusty, pustular lesions that ooze a foul cheese-like discharge. It is most noticeable in people with weakened immune systems. Scabies usually affects the arms, hands, and feet and can also cause severe itching. The rash may appear on the body, but the scabies infection can also affect the penis, scrotum, and breasts.
Treatment
To prevent scabies outbreaks, prevent close contact with infected people or items. Those items are generally clothing, towels, and bedding. If you think you have contact with an infected person, you should wash the item immediately. If you cannot pass the thing, you can store it in a plastic bag in your house for a few days or a week. If you suspect that you may have contracted scabies, consult with your health care provider to determine whether you need treatment.
The treatment of scabies can include applying a topical preparation containing ivermectin, permethrin, or benzyl benzoate. Some individuals will experience crusting and scaly patches. If you have these scabies outbreaks, you can consider oral ivermectin, although this medication isn't recommended for young children and pregnant women because it may cross the blood-brain barrier.
Prevention
Scabies is a contagious disease that affects more than 200 million people worldwide at any given time. It is common in hot, tropical climates and communities where many people live in close quarters. People of all ages, races, and gender can develop scabies, including babies and elderly people. In addition, those with impaired immune systems, such as those who have recently undergone organ transplants, are at increased risk of contracting scabies.
Diagnosing scabies is often challenging. The 2020 IACS Criteria are an attempt to establish diagnostic features that are robust and pragmatic. They will enhance consistency and standardization of scabies diagnosis in clinical and field settings. To develop these diagnostic features, an expert panel composed of dermatologists, epidemiologists, and other relevant medical professionals participated in a Delphi study to develop the criteria. The 2020 IACS Criteria categorize scabies cases into three levels of diagnostic certainty and eight subcategories. In addition, the guidelines include detailed definitions and illustrations for training.




