Melanoma Detection and Treatment
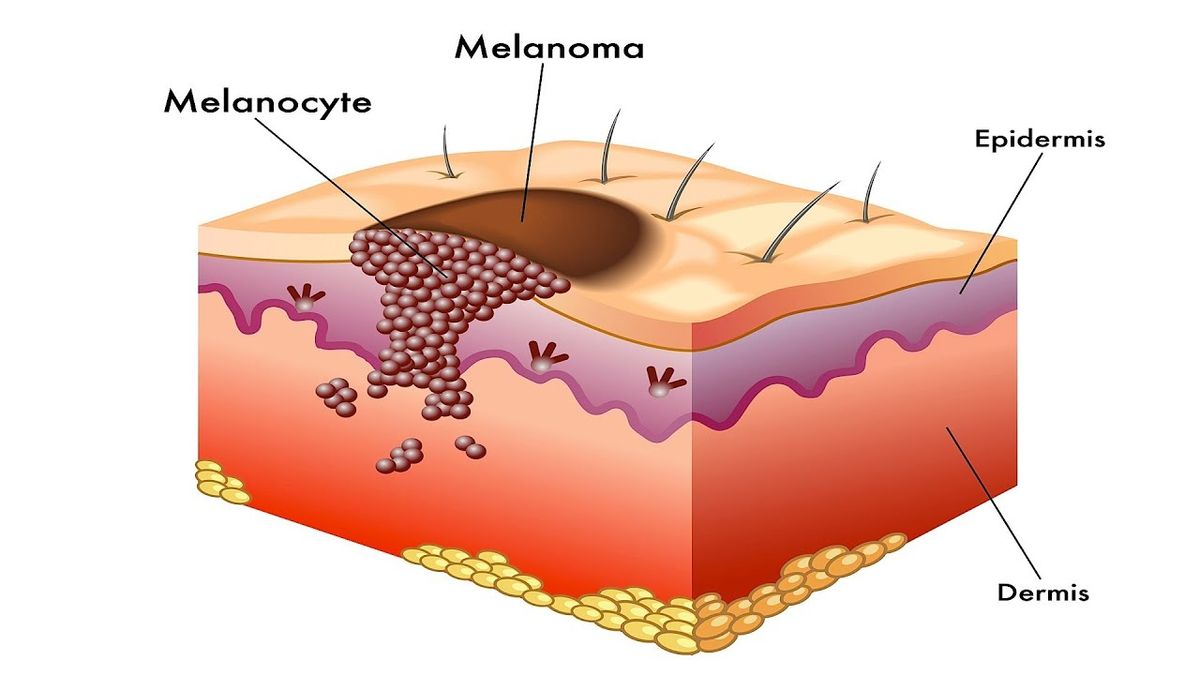
Early detection is the key to melanoma survival, so getting the disease detected early is vital. Fortunately, there are several effective treatments for melanoma. Treatment options include surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. While you may not receive a cure for melanoma, you can control the symptoms and relieve the pain. Several specialists are dedicated to helping those with cancer.
Detecting melanoma
Early detection of melanoma is essential for the survival of survivors. Melanoma can spread rapidly from the skin to other organs and is, therefore, the most deadly type of skin cancer. Although it can be treated with chemotherapy, detection is critical for survival. Patients with melanoma can live up to five years with proper care. If detected early, melanoma has a 99 per cent five-year survival rate.
Early detection is important because melanoma is curable if detected early. However, the survival rate is much lower when it is detected late. Early detection is the best defence against the deadly disease, and the best way to start your melanoma treatment is by self-observation. For more information on early detection, visit the War on Melanoma website of Oregon Health and Science University. The website also includes an e-module on melanoma detection.
Treatment options
There are many treatment options for melanoma. The earlier melanoma is detected, the easier it is to treat. However, treatment options for melanoma may differ from person to person. To make the process easier, you should have the opportunity to learn about these options and discuss them with your doctor. There are certain things to remember, however. A second opinion is highly recommended, just in case.
In most cases, the cancerous tumour is removed through surgery. Surgical removal is the most common way to remove the melanoma. This method works best when the melanoma has spread to only a few areas. While surgery can't cure the disease, it will reduce the pain and extend your life. There are some risks associated with the surgical removal of the melanoma.
Early detection
One of the easiest cancers to detect early is melanoma. This is because most melanomas occur on visible areas of skin or mucosa. This outward-facing property creates a wealth of opportunities for screening. Whole population screening programs, molecular tests, and cellular modalities can take advantage of this accessible area. The following are some of how early detection of melanoma can be improved.
First, patients should report any unusual naevi or skin changes that are not otherwise present. Early detection of melanoma is essential to optimize patient outcomes. In addition to routine skin exams, a patient's doctor should also look for suspicious lesions. The thicker the lesion, the lower the chances of survival. To assess the risk of melanoma, a physician can use dermatoscopy. If a lesion is suspicious, a physician may perform a biopsy to rule out melanoma. In some cases, the patient may need to have the rest of the body checked.
Cure
Researchers are investigating new ways to cure melanoma through targeted therapy. These therapies target specific genes and proteins found in cancer cells, limiting damage to healthy cells. Recent studies have uncovered genes and pathways implicated in melanoma development, allowing physicians to tailor treatment plans to patients based on genetic abnormalities. Researchers are also investigating the development of drugs that can block specific biochemical pathways in melanoma.
Immunotherapy research has focused on melanoma, one of the most mutated types of cancer. As such, melanoma has the greatest potential to trigger an immune response. Researchers are studying different types of immunotherapy, including a combination of immunotherapy and targeted therapies. However, while the race to cure melanoma is ongoing, a few promising approaches have already shown promising resulte




