Cardiovascular Disease in Africa
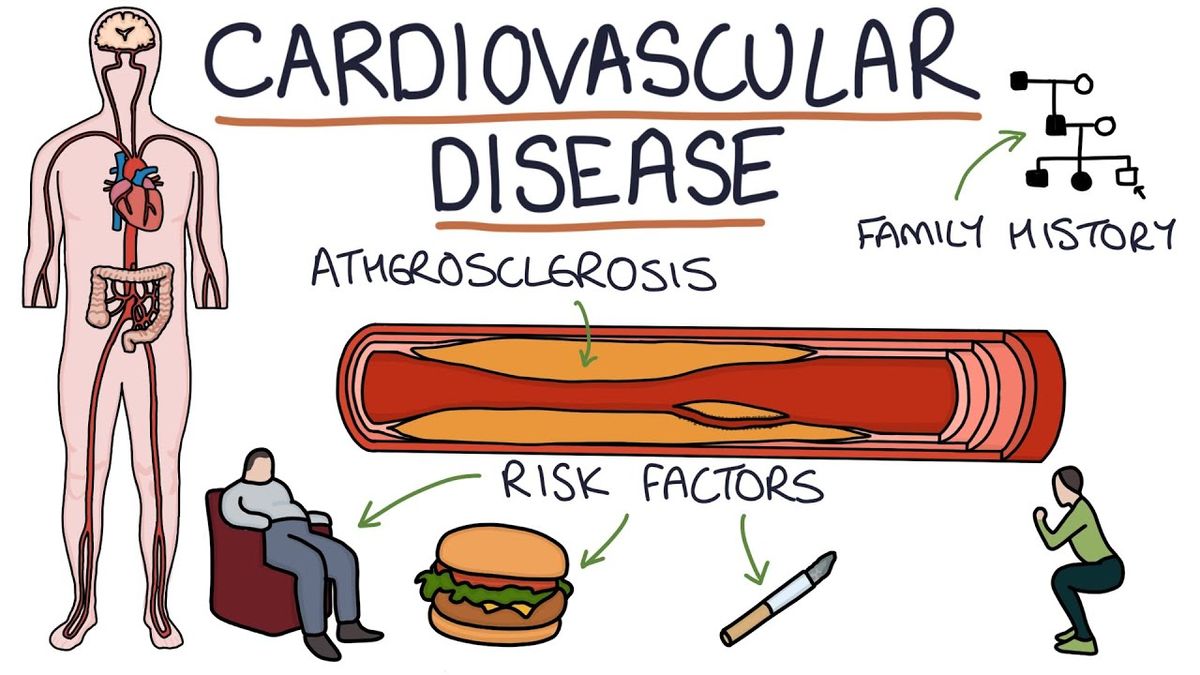
Cardiovascular disease is a group of diseases that can affect a person's heart. It affects different parts of the heart and can be caused by a number of different factors. Some of these diseases are coronary artery disease, which can lead to blockages and fluid buildup. Other types of cardiovascular disease include peripheral artery disease, which can lead to blockages and narrowing of blood vessels. There are also congenital heart defects, which affect different parts of the heart. Some of these conditions can cause fluid buildup or pericarditis, or other complications of heart failure and cardiovascular disease.
Stroke
Stroke and cardiovascular disease are both serious medical conditions that affect the heart and blood vessels. During a stroke, part of the blood flow to the brain is cut off, resulting in a lack of oxygen. This causes cells in the brain to die. These conditions are among the leading causes of death and disability among older adults. Fortunately, there are some warning signs of stroke or heart attack that can help you get the medical attention you need.
Although both men and women are at risk of a stroke, statistics show that men are more likely to experience one than women. Men tend to have heart attacks and strokes at a younger age, but women are more likely to die from a stroke. In the United States, there are 795,000 people who suffer a stroke each year. Nearly 155,000 people die every year from the disease. In New York State alone, 6,000 people die from a stroke. For more information about stroke statistics, you can visit the NYS Coverdell Stroke Quality Improvement and Registry Program.
Coronary artery disease
The symptoms of coronary artery disease include pain in the upper body, usually around the chest. They may also spread to the arms, neck, and back. If you experience these symptoms, you should immediately visit your doctor for a proper diagnosis. A doctor will use the electrocardiogram (ECG) to assess your heart's electrical activity and help you understand the cause of your symptoms.
Coronary artery disease occurs when the heart is not receiving enough oxygen-rich blood. As a result, it can lead to heart attacks and strokes. However, it is possible to decrease your risk by avoiding tobacco use, adopting a healthy diet, and increasing your physical activity. Also, regular blood tests can help you identify whether you are at risk for coronary artery disease.
Cerebrovascular disease
Cerebrovascular disease affects blood vessels in the brain and can cause a range of problems. The most common problems are stroke, vascular malformation, and aneurysm. If the blood vessels in the brain are damaged, brain cells will not get enough oxygen. This causes brain cells to die. The brain cannot repair itself, so treatment is needed immediately.
Lifestyle optimization is vital to prevent and treat cerebrovascular disease. Lifestyle strategies are not approved by the FDA, but they can improve your health and prevent the development of the disease. One of the first steps is cleaning up your diet. Try an anti-inflammatory nutrition plan that eliminates foods that trigger inflammation.
Coronary aneurysm
Coronary aneurysms are rare but life-threatening complications of cardiovascular disease. They occur when the walls of an artery become weakened and stretch, often leading to a rupture. A rupture can cause severe internal bleeding, and can also affect other major arteries.
Coronary aneurysms are relatively uncommon and usually discovered incidentally during angiography. They can be congenital or the result of connective tissue disorders or inflammatory diseases. In children, Kawasaki disease can lead to coronary aneurysms. Treatment options include surgical, percutaneous, and medical interventions. The optimal method of treatment depends on the type of aneurysm and the extent of its vascular damage.
Heart failure
Heart failure and cardiovascular disease are major causes of mortality and morbidity in many developing countries. In Africa, these conditions contribute to approximately 7% to 10% of hospital admissions. Efforts are needed to develop early detection methods and effective treatments for this disease. Prevention efforts also need to be improved.
Proper diagnosis and treatment can improve symptoms and lengthen life for some people. However, the severity of heart failure is unpredictable. If left untreated, patients may end up needing a heart transplant or a ventricular assist device.