The Microbiota Definition
Simply put, it is a community of living microorganisms, and each of us is a part of the ecosystem. This community has a unique composition and function and is considered a regional ecosystem. Microorganisms are beneficial to the human body and vital to our health and well-being.
Microbiota is a group of living microorganisms.
Microbiota is a term used to describe a collection of living microorganisms in a defined environment. This assemblage may include viruses, phages, viroids, and free DNA. Researchers have proposed that microbiota should include a broader scope of molecules produced by coexisting microorganisms.
It is a regional ecosystem.
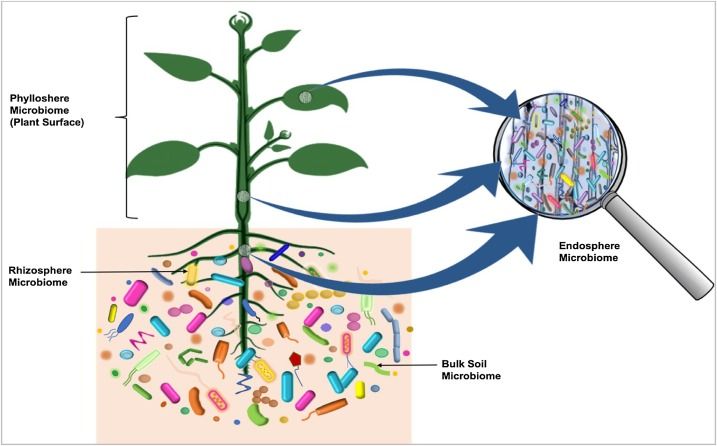
Microbiota is an essential component of soil ecosystems and plays a vital role in the functioning of the soil ecosystem. Many ecosystem services are dependent on the composition of microbial communities. Thus, considering microbial patterns at a regional scale will enable us to compare microbe patterns across diverse regions and subsisting habitats. Soil aggregates are mainly made up of micro and macro-organisms, which bind soil organic carbon and serve as filters to limit oxygen and water flow. These aggregates provide a unique ecological niche.
It is individual to each organism.
The microbiome concept is often used to describe the bacterial communities that colonize an organism. This concept is not uniform in all cases because bacterial communities perform different functions during different cycle stages. In some cases, the bacterial communities share the same niche, but the rest of the communities are individual to each organism.
It is a functional unit.
Microbiota is a functional unit that is essential for maintaining ecological balance. It regulates many biological processes and contributes to many ecosystem services. It can be studied in several different ecosystems, from nearby to distant environments. It primarily comprises micro-aggregates that bind soil organic carbon to macro-aggregates that limit water and oxygen diffusion. These microorganisms provide a specific ecological niche.
It affects health
In the early stages of life, the human microbiome can influence the development of certain diseases and health. Researchers have begun to explore the relationship between gut microbiota composition and health. Recently, the National Institutes of Health awarded $275,000 to study the microbiome in the skin, gut, and nasal regions. The team hopes to identify the bacteria that may contribute to airway disease.
It is affected by environmental factors.
Environmental factors are known to affect the microbiota of humans in various ways. They profoundly affect various microbiome aspects, including bacteria and fungi's structure and function. Humans are exposed to many environmental factors, including air, water, soil, and food. These factors have an impact on human health and disease. Different environmental factors can affect the microbiota, including the physical environment, social factors, and dietary factors.
It is a source of prebiotics.
Your microbiota is a collection of bacteria that live in your digestive tract. These bacteria help you digest food and fight inflammation. They also help your immune system work properly. Adding prebiotics to your diet may help these bacteria function better. Dietitian and digestive disease researcher Gail Cresci explains how prebiotics work and why they are important.



