"Pulse Points: Decoding the Heart Attack Letter"
"Learn about heart attacks: understand their causes, symptoms, prevention, and treatment strategies for better heart health. No prior medical knowledge required
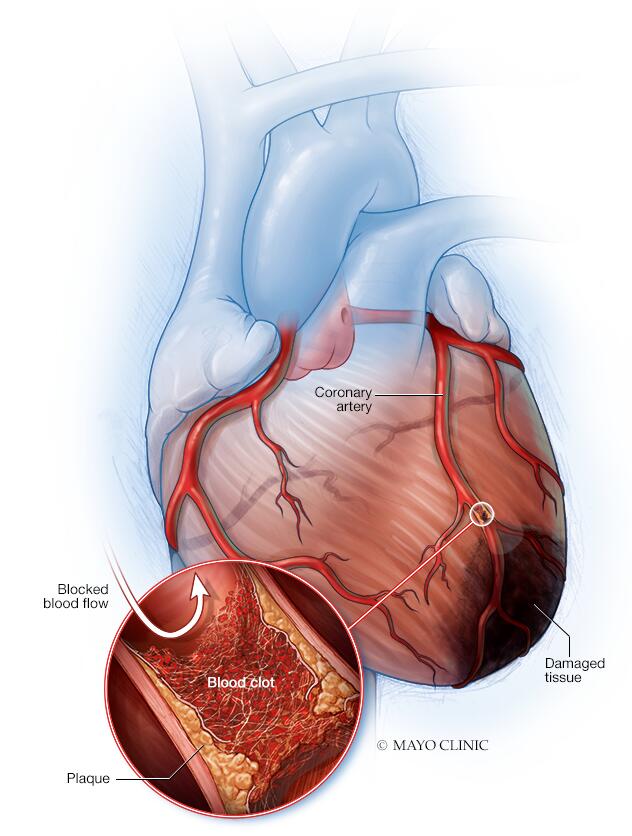
A heart attack, medically termed as myocardial infarction, is a severe health condition that primarily occurs when the blood supply to the heart muscle is obstructed, usually by a blood clot. This can damage or destroy part of the heart muscle, leading to life-threatening complications or death. Although a heart attack can strike without warning, understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment strategies can significantly enhance survival rates and quality of life.
The main cause of a heart attack is coronary heart disease, a condition in which the coronary arteries (the major blood vessels that supply blood, oxygen, and nutrients to our heart) become clogged with deposits of cholesterol, known as plaques. When a plaque ruptures, it can cause a blood clot to form and obstruct the blood flow. This sudden blockage that deprives the heart muscle of essential oxygen and nutrients results in a heart attack.
The most common symptom of a heart attack is chest pain or discomfort, often described as a feeling of tightness, pressure, squeezing, or aching in the chest. This discomfort can sometimes spread to other parts of the body, such as the arms, neck, jaw, back, or abdomen. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, lightheadedness, nausea, extreme fatigue, and cold sweats. It is important to note that symptoms may vary and some people may experience mild symptoms, while others may have more intense manifestations.
If you or someone else is experiencing these symptoms, it is crucial to seek immediate emergency medical attention. The sooner treatment is initiated, the better the chances of limiting the amount of damage to the heart muscle and enhancing the prognosis.
Upon reaching hospital, doctors will conduct a series of tests to diagnose a heart attack. These tests may include an electrocardiogram (ECG), blood tests, a chest X-ray, or a coronary angiogram. Treatment options for a heart attack primarily aim to restore blood flow to the heart muscle as soon as possible, and may include medications, coronary angioplasty and stenting or coronary artery bypass surgery.
After a heart attack, it is vital to prevent another one. This usually involves lifestyle changes, cardiac rehabilitation, medications and, in some cases, surgical procedures. Lifestyle changes can include quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, getting regular physical activity, controlling blood cholesterol and sugar levels, and managing stress.
In conclusion, a heart attack is a serious medical emergency that requires immediate attention. Being alert to the signs and symptoms and seeking prompt medical care can significantly improve outcomes and survival rates. Moreover, adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle plays a key role in preventing heart attacks and promoting overall cardiovascular health.



