Lymphatic Drainage For Breast
If you are suffering from lumpy breasts and milk ducts, lymphatic drainage is one of the best ways to get relief. It is an easy technique to follow and should not cause any pain. Using this technique will help drain milk faster and ease any pain. However, it is important to use this technique properly. You can either breastfeed or use an unsupported breast pump.
Reduction therapy
Reduction therapy for lymphatic drainage for breast cancer patients involves hands-on therapy that promotes lymph flow and reduces swelling. This treatment is often part of a multimodal regimen, including compression bandaging, lymph-reducing exercises, and skin care. In one study, women who received intensive compression bandaging experienced a 30% to 37% reduction in swelling.
Reduction therapy for lymphatic drainage for breast cancer patients is an effective treatment option that can significantly reduce upper-limb lymphedema. It involves compression bandaging and manual lymphatic drainage using specialized pumping techniques. Manual lymphatic drainage is believed to increase lymph flow by causing superficial contractions in the skin. Many doctors now prescribe manual lymphatic drainage as a standard treatment for lymphedema patients, especially in European hospitals.
Maintenance therapy
Maintenance therapy for lymphatic drainage for the breast is an important component of breast cancer care. It involves continuing treatment at home to maintain the gains from phase I. This therapy typically involves self-lymph drainage, lymphatic exercises, skin care regimens, and compression bandages. This type of treatment is most effective when carried out regularly and continues for an extended period.
The Casley-Smith method involves a series of small effleurage movements using the side of the hand. This method is not recommended for acute inflammation caused by pathogenic germs because manual lymph drainage is likely to spread germs and cause blood poisoning (sepsis). The pressure applied to the breast varies based on the underlying tissue, but the hand movements are slow and repetitive. In areas with fibrosis, deeper movements and compression therapy are used.
Dos and don'ts
There are several dos and don'ts to lymphatic drainage for breasts. Patients should undress completely before the treatment. Tight clothing, including underwire bras, will interfere with the drainage process. Instead, choose comfortable cotton underwear without zippers, buckles, or pockets. Avoid wearing v-neck t-shirts with collar bones that protrude from your breasts. You should also wear loose-fitting clothing so the lymph vessels can circulate freely. Finally, be sure to follow a low-sodium diet for optimal results.
A trained massage therapist can perform lymphatic drainage on you. The massage involves applying light pressure to the affected areas in a stroking motion. This will stimulate the lymph vessels and move the fluid from swollen areas. Damaged lymph nodes or certain illnesses cause lymphedema. It usually manifests itself in the legs and arms.
ARM nodes
The ARM procedure is a surgical procedure to preserve upper-limb lymph nodes and lymphatics and reduce the effects of lymphoedema. It involves identifying ARM nodes in the upper outer quadrant of the axilla, lateral to the ascending lateral thoracic vein, which terminates in the axillary vein. Studies have shown that the ARM procedure reduces the incidence of upper-limb lymphoedema while preserving the upper-limb lymphatic system.
The ARM procedure is not a substitute for mastectomy, but it may offer a better alternative to mastectomy for certain types of cancer. The ARM lymphatic drainage channel is common to breast lymphatic flow. Surgical removal of the ARM lymph node may result in metastasis in the breast. This may be dangerous for patients with cancer in the axilla.
Preaortic lymph nodes
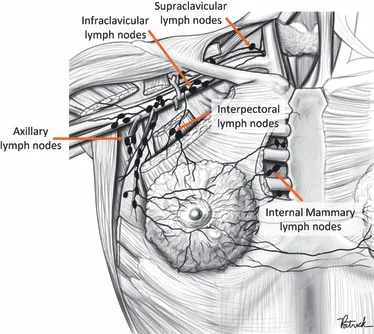
The lymphatic drainage for breasts consists of three main pathways. The left breast drains through the thoracic duct, while the right breast drains into the right subclavian vein. There are also sporadic drainage pathways to the subscapular nodes and rectus sheath.
The lymphatic system plays a vital role in fluid homeostasis and systemic immunity. It transports tissue fluid back to the blood, which makes it an important component of breast cancer treatment. Tumor metastasis occurs when malignant cells travel within the lymphatic system. As a result, evaluating lymphatic tissue is essential to cancer staging and prognosis. In addition, proper drainage of the lymphatic system can improve the patient's overall survival.



