Lupus Symptoms in Women
If you suspect you have lupus, you should visit your doctor for a proper diagnosis. You can get a prescription for lupus, or you can take OTC pain pills. However, you should consult a physician if the pain does not disappear. One of the most common symptoms of lupus is fever, which is caused by inflammation and can occur at any time. The fever is generally low-grade and may return to normal without medication.
Symptoms
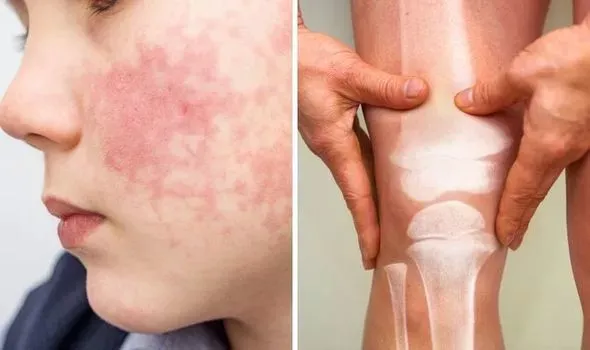
Lupus symptoms in women are many and varied. They can range from a butterfly rash to joint aches and swelling. They can also include chest pain and problems with the kidneys. Women can also experience fatigue and brittle hair that won't grow back. Many women also experience vaginal dryness and irregular periods. Some people can also experience pain or swelling in the face, neck, or arms.
Lupus is an autoimmune disease that affects the immune system of a woman. While men and women both experience lupus symptoms, women are most susceptible to developing it if they are of childbearing age. Women of color and those with sun-exposed skin are at higher risk of developing lupus symptoms.
If you think you are experiencing lupus symptoms, it is important to note them. Taking note of each symptom's onset, duration, and severity will be helpful when you meet with a doctor. It's also important to note other information, such as family history. In some cases, lupus is hereditary, which makes it even more important to be screened for the disease.
Treatments
The treatment for lupus can vary, but most patients will see improvement after the first round of treatment. The main goal of lupus treatment is to control the disease. Several types of medications can help women live pain-free life. However, some of these medications can cause side effects. If you are taking prescription medications, discussing the side effects with your doctor is important.
Lupus can cause severe complications, including inflammation of the heart and lungs. Patients may experience chest pain and an increased risk of clotting and bleeding. The disease can also damage the valves and heart muscles. Additionally, patients with lupus have an increased risk of developing coronary artery disease. Depending on the severity of the disease, treatments can include medications to increase the effectiveness of the heart and nervous system.
Besides prescription medications, some women can learn how to manage the disease with lifestyle changes. A well-balanced diet is best for lupus patients, with moderate amounts of fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and fish. Some doctors will also prescribe immunosuppressive medicines to control the disease's symptoms. These medicines may affect the immune system, so a health care provider should discuss the changes with you.
Risk factors
Women with lupus have an increased risk of pregnancy complications. Antiphospholipid antibodies can cause blood to clot in the placenta, increasing the risk of miscarriage. Women with active kidney disease also have a higher risk of preeclampsia, which can cause high blood pressure and fluid buildup in the womb. In addition, pregnant women taking corticosteroids are at risk of gestational diabetes and high blood pressure.
Alcohol consumption is another risk factor for lupus. Women who drink alcohol regularly have a lower risk than women who never drink. This is consistent with previous studies that found moderate drinking reduces lupus risk. Although the researchers didn't find any causal relationships between drinking alcohol and lupus, they did find that women who drank at least four drinks a week had a lower risk.
Other risk factors for lupus in women include ultraviolet light from the sun and exposure to certain chemicals. Studies have also suggested that female hormones play a role. Some researchers believe that the hormone estrogen may play a role in the development of the disease.




