'Heart Attack Letter: Envelope of Emergency Understanding Unsealed'
Learn about heart attacks: causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention. Find out how to protect your heart health and live a healthier life.
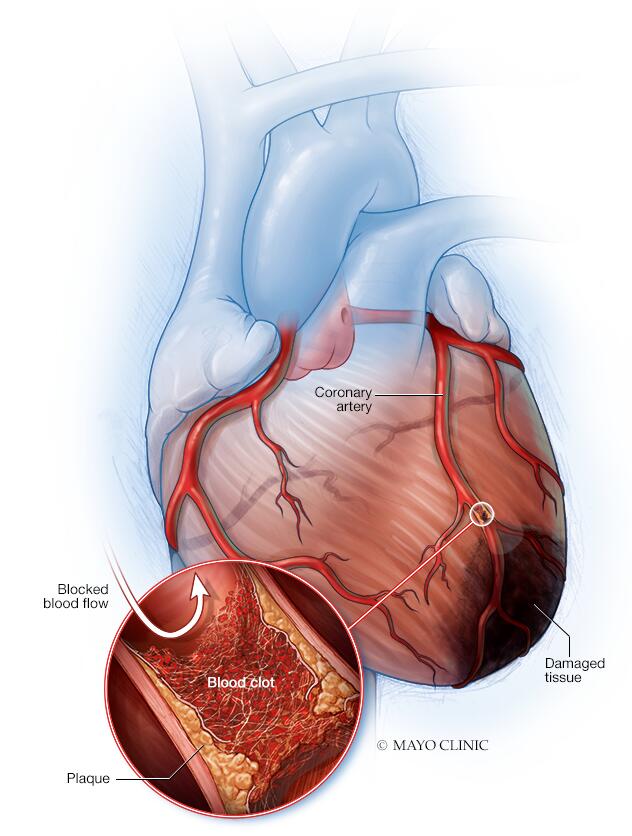
A heart attack, medically known as a myocardial infarction, is a severe medical emergency that occurs when the supply of blood to the heart is abruptly blocked, usually by a blood clot. The disruption of blood flow can damage or destroy part of the heart muscle, causing distressing symptoms and potentially leading to life-threatening complications. It's crucial to recognize the signs of a heart attack and seek immediate medical assistance.
The symptoms of a heart attack can vary from person to person. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort, often described as a crushing pressure, squeezing, or sensation of fullness in the center of the chest. This discomfort may last for more than a few minutes or go away and come back. However, not everyone who has a heart attack experiences chest pain. Other symptoms can include shortness of breath, nausea, vomiting, lightheadedness, cold sweat, and discomfort in other areas of the upper body such as the arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach.
Several factors can increase the risk of a heart attack. These include age, smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, obesity, diabetes, family history of heart disease, lack of physical activity, and an unhealthy diet. While some risk factors like age and family history cannot be changed, many others can be managed through lifestyle modifications and medical treatment. It is therefore crucial to lead a healthy lifestyle and manage any underlying health conditions to lower your risk of a heart attack.
If you or someone else is experiencing symptoms of a heart attack, it's essential to act quickly. Delay in treatment can lead to greater damage to the heart muscle. Call for emergency medical assistance immediately. While waiting for the ambulance, it may be helpful for the patient to rest in a comfortable position and try to stay calm. If aspirin is available and the person is not allergic to it, it can be given to the patient to help prevent further blood clotting.
Upon arrival at the hospital, the medical team will work quickly to restore blood flow to the heart. This may involve medications to dissolve blood clots, surgical procedures to open blocked arteries, or other treatments. After a heart attack, a period of rehabilitation is often necessary to help the patient recover and reduce the risk of future heart attacks. This may include medications, lifestyle changes, cardiac rehabilitation, and sometimes counseling.
A heart attack is a significant event, but with prompt treatment and good follow-up care, many people can return to their normal lives and enjoy a good quality of life. It's important to remember that having a heart attack means you are at higher risk of having another one. Therefore, it's crucial to take your medications as prescribed, attend all follow-up appointments, and make necessary lifestyle changes to minimize this risk.



