Diving Deep into Testosterone Therapy: Can You Hit the Pause Button?
Explore the implications of starting and stopping testosterone therapy, including potential health effects and considerations.
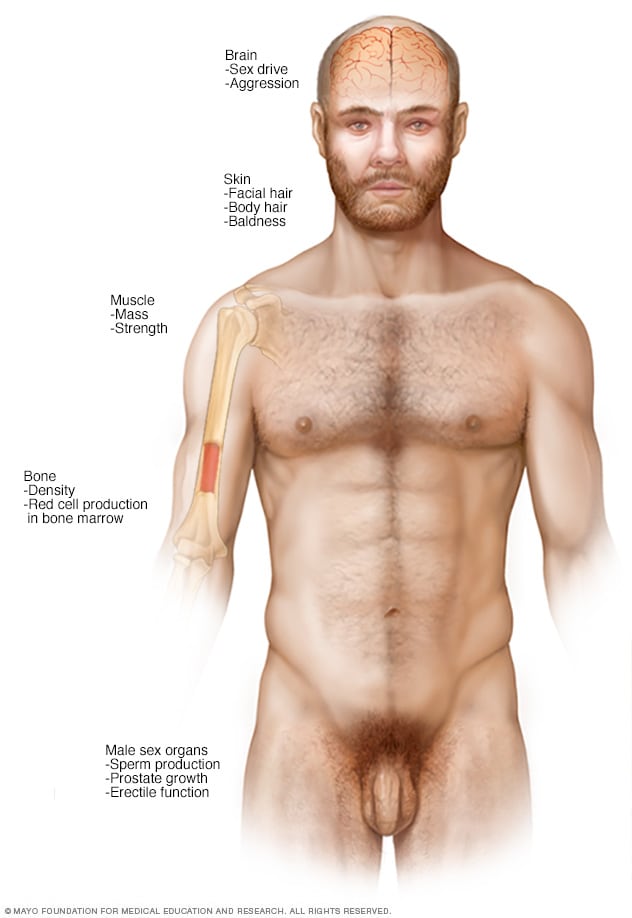
Testosterone therapy is a common and effective treatment for those suffering from low testosterone levels, often associated with symptoms like fatigue, mood changes, diminished sex drive, and difficulty with concentration. While it's a widespread and influential tool, some might wonder what happens once treatment has begun: is it possible to stop? The answer is both yes and no, and it largely depends on the individual's circumstances.
Firstly, it's essential to understand that testosterone therapy is, in most cases, a lifelong treatment. Testosterone levels naturally decline as men age, and for those who have started therapy because of age-related decline, ceasing treatment will likely lead to the return of symptoms. In this scenario, stopping therapy might not be the best course of action.
However, in other cases, such as when an individual starts testosterone therapy to aid in gender transition, the course of treatment might not be lifelong. In these cases, stopping testosterone therapy can have different effects, depending on how long the treatment has been administered and at what dosage. Early changes, like the deepening of the voice and increased body and facial hair, may not revert after stopping testosterone therapy. Longer-term changes, such as clitoral enlargement and menstrual changes, may or may not be reversible.
If an individual wishes to stop testosterone therapy for any reason, it's imperative to do so under the guidance of a healthcare provider. Abruptly stopping testosterone therapy can lead to withdrawal symptoms such as fatigue, depression, irritability, loss of appetite, insomnia, and decreased libido. To avoid withdrawal symptoms, doctors will often recommend a process called 'tapering'. Tapering involves slowly reducing the dosage over time, allowing the body to gradually adjust to the decrease in testosterone levels.
In some cases, people might want to stop testosterone therapy due to side effects. It's worth noting that while side effects can occur, they are typically manageable under proper medical supervision. Common side effects include acne, oily skin, mild fluid retention, stimulation of prostate tissue leading to increased urination, breast enlargement, worsening of sleep apnea, decreased testicular size, mood swings, and increased bad (LDL) cholesterol. It's important to discuss any side effects with your healthcare provider, as they can often adjust your dosage or switch you to a different form of therapy to mitigate these issues.
Overall, the decision to start or stop testosterone therapy should be made in close consultation with a healthcare provider. The benefits and potential risks must be weighed carefully, and the decision should be based on individual needs, health status, and personal circumstances. Testosterone therapy can be a transformative tool for many, but it's essential to approach it with a full understanding of what it entails and the possible implications of starting or stopping treatment.



