Cracking the Code: Decoding the Heart Attack Letter Phenomenon
Learn about heart attack causes, symptoms, treatments, and prevention tips from a medical expert, protecting your cardiovascular health for a longer life.
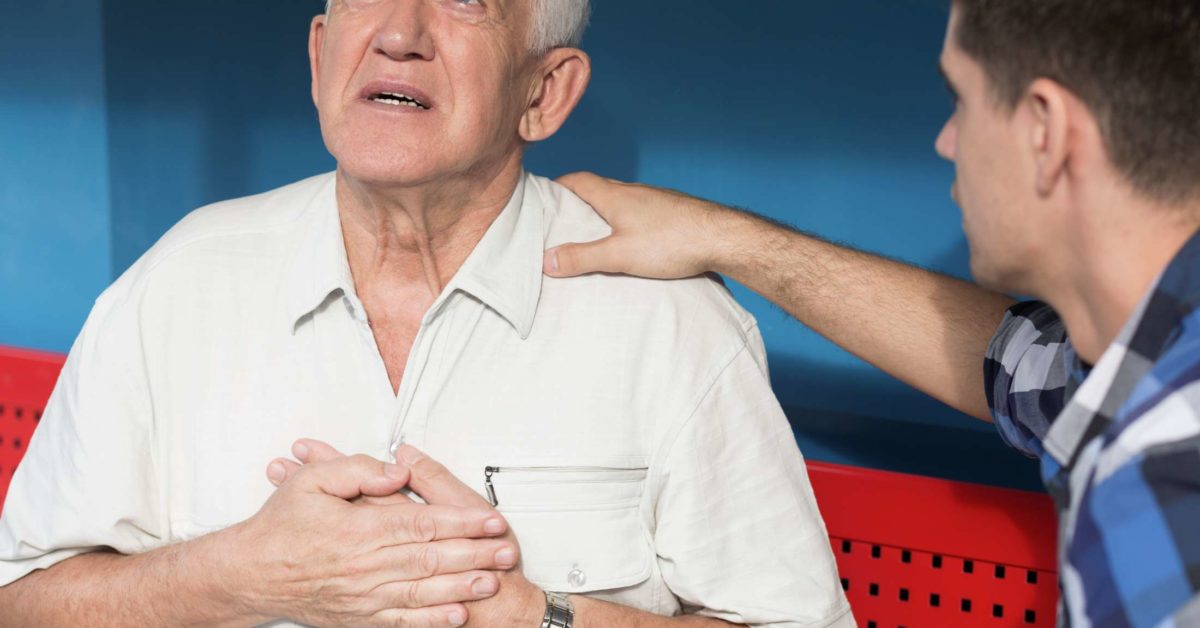
Heart attacks are a significant health concern that affects millions of people around the world. They can be both life-altering and life-threatening, making it essential for individuals to understand what they are, the risk factors associated with them, and how to take preventative measures. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of heart attacks, including their causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
A heart attack, also known as a myocardial infarction, occurs when the blood supply to part of the heart muscle is severely reduced or completely blocked. This is typically a result of a blood clot that forms in a coronary artery, which is responsible for supplying oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle. When the heart muscle is deprived of oxygen, it can become damaged or die, leading to serious health complications or even death.
There are several risk factors that can increase an individual's likelihood of experiencing a heart attack. Some of these risk factors include age, gender, family history, smoking, hypertension, high cholesterol, obesity, diabetes, and stress. Additionally, certain lifestyle choices and habits can contribute to an increased risk of a heart attack, such as consuming a diet high in saturated fats, living a sedentary lifestyle, and excessive alcohol consumption.
Recognizing the symptoms of a heart attack is crucial, as early detection and treatment can significantly improve one's chances of survival and recovery. Some common symptoms of a heart attack include chest pain or discomfort, which may feel like pressure, squeezing, or fullness; shortness of breath; nausea or vomiting; lightheadedness or fainting; cold sweats; and discomfort in the arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach. It's important to note that not all heart attacks present with these classic symptoms, and some individuals may experience no symptoms at all. This is especially true for women, who may experience more subtle or atypical symptoms.
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of a heart attack, it's crucial to seek medical attention immediately. Call emergency services right away and wait for their arrival. While waiting, the person experiencing the heart attack should try to remain as calm and still as possible to conserve their energy.
Treatment for a heart attack generally focuses on re-establishing blood flow to the affected area of the heart muscle and preventing further damage. This may involve medications to break up or prevent blood clots, reduce heart workload and oxygen demand, and treat arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats). In more severe cases, medical procedures such as angioplasty, stenting, or bypass surgery may be necessary to restore blood flow.
Recovering from a heart attack can be a challenging process, but with the appropriate care and lifestyle changes, many individuals can return to their normal activities and even improve their overall heart health. Rehabilitation programs, also known as cardiac rehab, can provide guidance on exercise, diet, and stress management, helping patients regain strength and confidence in their daily activities. Medications may also be prescribed to help manage risk factors and prevent future heart attacks.
While heart attacks are a serious health concern, understanding the risk factors, recognizing symptoms, and receiving prompt medical attention can greatly improve one's chances of survival and recovery. By taking preventative measures and maintaining a heart-healthy lifestyle, individuals can reduce their risk of experiencing a heart attack and live a longer, healthier life.





