Ca 199 Elevated in GI Malignancies
Read on to learn more. Below are some causes, symptoms, and test results for Ca 199 elevation. This article can also help you decide whether to seek further diagnostic testing for Ca 199 elevation. In addition, it will give you a better idea of what to expect from the test results.
Ca 199 elevate in GI malignancies?
Patients with gastrointestinal malignancies may have elevated levels of the cytokine CA 19-9, which is typically measured every one to three months. Patients who undergo potentially curative surgery or chemotherapy should be monitored for CA-19-9 levels. Elevated CA 19-9 levels usually precede the radiographic appearance of recurrent disease, so further investigation should be carried out. This marker may be elevated in gastrointestinal conditions, including gastric cancer, pancreatitis, and cirrhosis. It can also be elevated in patients with diseases of the bile ducts, such as gall bladder and biliary tract obstruction.
CA 19-9 is a tumour marker particularly sensitive for hepatobiliary and pancreatic cancer. The highest CA 19-9 serum levels have been reported in patients with pancreatic and hepatobiliary malignancies. However, despite its sensitivity, the exact role of CA 19-9 in GI malignancies is still unknown. One patient with gastric adenocarcinoma study found a 17.3% immunopositivity rate.
Mechanisms of Ca 199 elevation
Moderate elevations of CA 19-9 are considered benign, while very high levels are associated with malignancies. However, previous studies have indicated a correlation between elevated CA 19-9 levels and cancer. Some researchers have documented highly elevated serum levels of CA 19-9, which reached 187,000 U/mL and subsequently normalized after biliary patency. The most likely cause for this elevated CA 19-9 level remains unclear, but other possible mechanisms may be involved.
The synthesis of CA 19-9 is a normal function of bronchial epithelial cells. However, when the epithelial cells of the bronchioles become inflamed, extravasation of mucus glycoprotein may result in elevations of CA 19-9. Although the association between chronic lung disease and elevated levels of CA 19-9 remains unclear, it is believed to be associated with inflammatory processes in the lung tissue. Earlier, it was proposed that elevated levels of CA 19-9 could act as biomarkers for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, a disorder often characterized by progressive lung disease.
Detection methods
While elevated levels of CA 19-9 can indicate cancer, they are not always the only indication of the disease. This is because a variety of factors can impact the level of this molecule, including the stage of the disease, any coexisting conditions, and the patient's overall health. Also, elevated levels of CA 19-9 can indicate the disease's recurrence or re-occurring disease.
One study conducted in 2004 looked at serum CA 19-9 levels as a diagnostic marker for pancreatic cancer. It found that CA 19-9 serum levels were elevated in 70% to 80% of patients with this disease. The authors also noted that elevated serum levels of CA 19-9 may indicate other conditions, such as extrapancreatic malignancies or benign hepatopancreatic biliary disorders. Thus, the CA 19-9 test has less sensitivity as a diagnostic marker and is best used alongside other tests and imaging techniques.
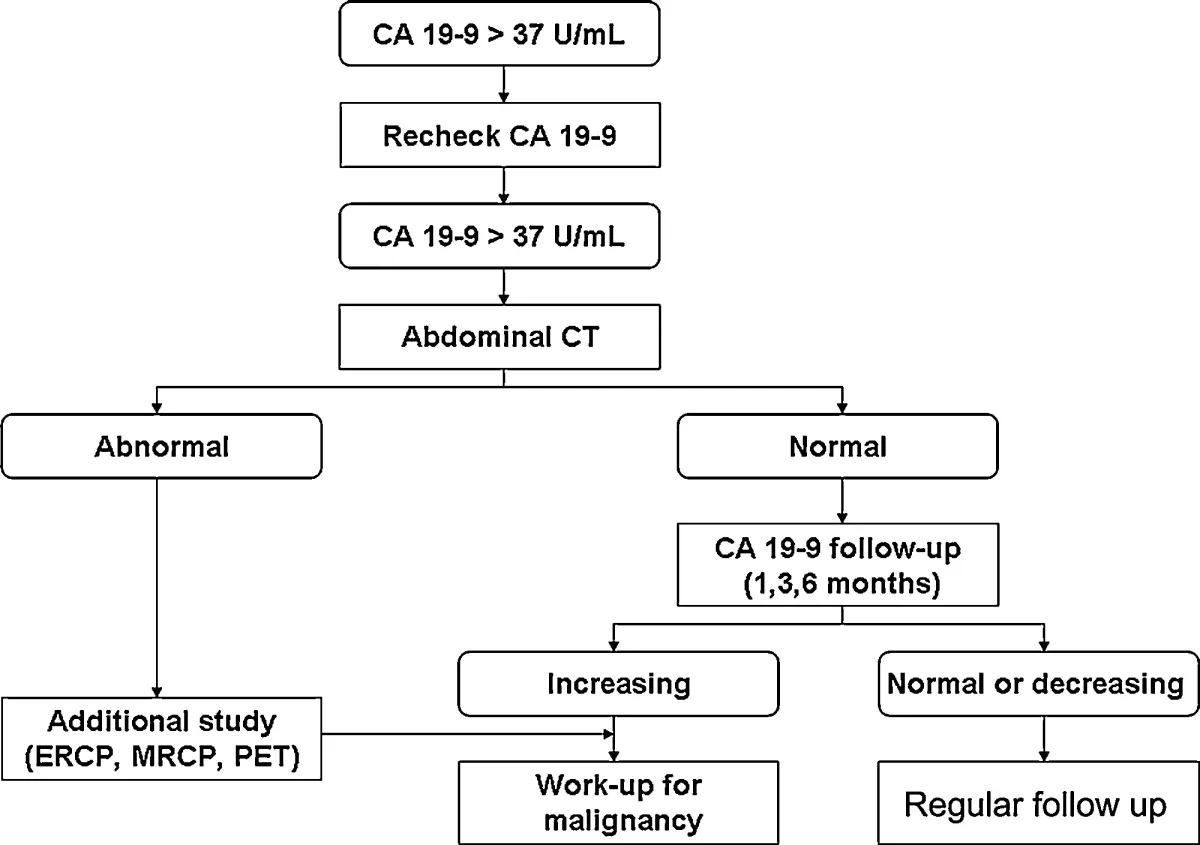
Test results
CA 19-9 blood levels are often elevated in pancreatic cancer patients but can also occur in cases of other types of cancer and gall stones. In some rare cases, they may also be elevated in healthy individuals. A vein in the arm is inserted to collect a blood sample. There is no special preparation required to obtain a high-quality piece. The test results are used to monitor the progress of pancreatic cancer or to watch for recurrence.
Patients with a low level of CA 19-9 may still benefit from testing to determine if cancer has spread. However, elevated CA 19-9 levels may also signify a more advanced stage of the disease. Cancer patients with an elevated CA 19-9 level may benefit from a more aggressive treatment plan. Cancer patients may also benefit from a CA 19-9 test and other tests to determine the cause of the elevated levels.




