Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia
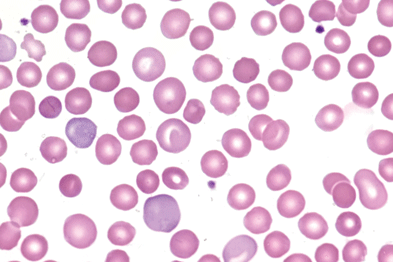
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia is a disease that affects the body's blood cells. Various blood tests can be used to determine whether or not you have the disorder. Blood tests may include a peripheral smear, a sample of blood examined under a microscope, and a reticulocyte count, which measures the number of young red blood cells in the body.
Idiopathic autoimmune hemolytic anemia
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia is a condition in which a person's immune system destroys the red blood cells of a patient. This disease occurs in individuals with a normal blood cell system, although it may be secondary to another disorder. It may also occur without a precipitating factor. The condition is often short-lived.
There are several different types of autoimmune hemolytic anemia. Autoimmune hemolytic anemia is rare and can be treated by a healthcare provider. However, this disorder can become very serious and even lead to death if untreated. Therefore, it is important to get prompt medical treatment if you suspect you might have AIHA.
Treatment options
There are several treatment options for autoimmune hemolytic anemia, including blood transfusions. These procedures increase the number of red blood cells responsible for carrying oxygen to the body's tissues. Other treatment options include corticosteroids, which can suppress an overactive immune system and limit the destruction of red blood cells. In some cases, patients may also be given immune globulins. These treatments may cause lightheadedness or a high fever. Another option is an exchange transfusion, which removes damaged blood cells and replaces them with healthy ones.
Treatment options for autoimmune hemolytic anemia depend on the severity of the condition. Patients with mild cases of AIHA may not need any treatment at all. However, more severe cases may require multiple lines of therapy. Your healthcare provider can run tests to assess your condition and recommend the best treatment options.
Symptoms
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA) is a disease where the body attacks its blood cells, which can cause anemia. There is no known cause, and treatment usually consists of treating the underlying disease. Depending on the severity of the disease, a patient may need to undergo a splenectomy to prevent the destruction of red blood cells. Blood transfusions are also necessary but should be performed with extreme caution.
The symptoms of autoimmune hemolytic anemia can vary from mild to severe and can be life-threatening if left untreated. Your healthcare provider can perform several tests to determine the severity of the condition and recommend the appropriate treatment.
Causes
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA) is a rare disorder in which the immune system mistakenly attacks red blood cells, resulting in a drop in red blood cell count and anemia. This disease can be mild or severe, and the symptoms may occur suddenly. Treatment may include corticosteroids, immunosuppressive drugs, or blood transfusions, depending on the severity.
There are several causes of autoimmune hemolytic anemia, which are all related to the immune system. While the infection is the most common, other illnesses such as cancer, lupus, or an Epstein-Barr virus can also lead to this disorder. In addition, certain drugs may cause hemolytic anemia.



